Home » [The LoopVOC Playbook] Using Customer Feedback to Drive Your Product Roadmap
[The LoopVOC Playbook] Using Customer Feedback to Drive Your Product Roadmap
Madeline Turner

Building a product that stands out in the B2B marketplace has never been more difficult.
Competition is high. Technology is constantly changing. And customer expectations require innovation. Having a good product vision is critical to success.
Keeping up with market demands means having a product team that is acutely attuned with how customers are using the product today, and how they will want to be using the product tomorrow. This level of synchronicity can’t happen without processes that keep customer feedback central to product development. Customer feedback is becoming more crucial to product management every year.
Oftentimes, however, customer feedback is only prioritized as products are being developed and then not again until after there’s a problem or a new feature is in production. Customer feedback is not included in the initial product strategy and internal stakeholders like a development team are not always aware of customer requests.
The problem with this model is that we’re setting ourselves up for failure—either we won’t be able to respond quickly enough or we’re developing our products without input early enough.
This nets out to wasted time and resources. Something nobody wants when they create a product.
Product teams need a better way to incorporate customer feedback when creating a product roadmap—from concept-to-recycle.
LoopVOC exists to centralize customer feedback in real time so that all teams have the opportunity to listen, understand, and respond based on the greatest risks and opportunities to your business.
This product roadmap playbook will help your team understand how to use LoopVOC to:
- Listen for user feedback across channels
- Identify and understand product issues
- Benchmark customer feedback against competitors
- Adapt product strategies to improve results
1. Listen for customer feedback across channels
Whether you’ve identified a problem with declining sales and retention, want to proactively ensure that your R&D strategy is competitive, or understand whether customers are finding value in new releases—the first step is to collect customer feedback.
When talking about product adoption and customer experience with our products, customer feedback includes both how our customers talk about our products as well as how our customers use our products.
When we think about usage, we’ll look at KPIs that tell us things like:
- Have users used the product or feature?
- Have they used the product or feature more than once?
- Are they using the product or feature as intended?
- Are they running into unexpected roadblocks when using the product or feature?
In addition to monitoring user behavior in-platform, you’ll want to collect feedback across the places your customers are already sharing and engaging about your product.
One of the best (and growing) channels for B2B customer feedback is online review sites. Customers are regularly sharing feedback about their experience and product features that are critical for product teams to pay attention to. Because of how these sites are structured, you can learn what customers love and what they don’t love about experience with your product.
Feedback shared on review sites will also give you insight into where customers place the most value.
Additional Public Channels to monitor:
- Social Media Posts and Groups
- Customer Communities and Online Forums
- Email listservs
- Public Slack Channels
Qualitative NPS feedback is another critical channel for product feedback.
In addition to asking customers whether or not they’re likely to recommend your company or product, ask them about the product features most important to them. Understanding the feedback driving the Net Promoter Score, and where customers are finding the most value in your products, will guide your product development strategies and help you build features your customers want.
Additional Internal Feedback Channels:
- Customer Support Tickets (are there common issues with critical features that could be impacting the value customers receive?)
- Customer Success calls (are customers regularly talking about product stability, analytics, or feature requests?)
- Sales Calls (are their key features or integrations missing in your product that are impacting sales?)
- CSAT, and Win/Loss surveys (are competitors winning more deals?)
Connect your customer feedback in Loop
Once you’ve identified your feedback channels, you’ll want to connect this feedback in Loop. This step is easy, but it’s the most important step of all.
Using natural language processing, Loop extracts meaningful insights from customer feedback, so that marketing and product leaders can proactively identify issues impacting revenue, and pivot product initiatives to address them.
Your feedback data is what makes it possible for Loop to run its magic and extract real-time insights.
- Select the feedback channel you would like to integrate with.
- Complete the steps for adding your feedback data.
- Your data will be automatically cleaned, tagged with trends, and integrated into Loop.
2. Identify and understand the problems impacting revenue
Once your feedback has been connected in Loop, the next step is to identify any potential feedback trends related to your product strategy: ease of use, features, platform, or analytics.
Step 1: Review the topics related to product, and identify those with a high amount of positive or negative feedback.
- Ease of Use: How adaptable is the user interface? Does it take a lot of resources to understand how to use the tool?
- Features: Which capabilities of your product are most important to users? Which features are lacking? Missing altogether? Overkill?
- Platform: Has platform stability impacted customer retention? Are users looking for greater accessibility? More integrations? Greater security?
- Analytics: How well does your product interpret and visualize data into insights? How well can users build reports and search for the information they need?
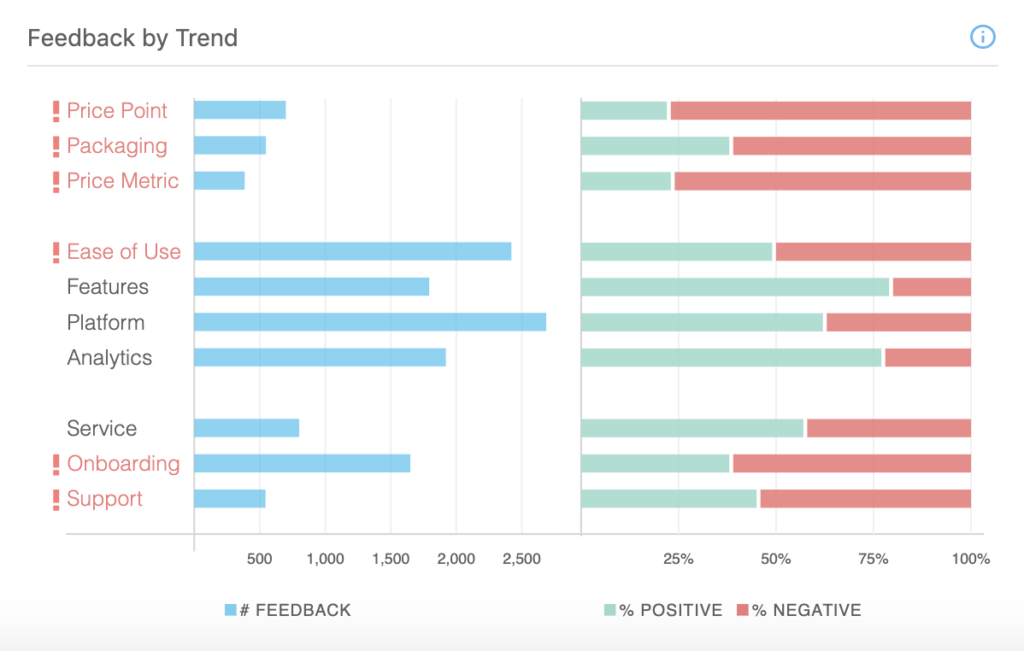
(For the sake of this exercise, we’ll drill into Ease of Use. But you can also see playbooks for addressing negative feedback related to Pricing or Support here.)
We can see that feedback related to Ease of Use is trending negative. Our next step will be to understand the root cause of this feedback and how long feedback related to Ease of Use has been trending negative.
It is also worth noting here that no issue in the customer experience is isolated. If customers are having issues using your product, this pain point will impact their feedback related to onboarding (are they adequately trained to use the product?), support (are they getting the help they need when they run into issues using the product?), and even pricing (is usability impacting the value they’re receiving from the product?).
Once we understand the issues customers are experiencing related to Ease of Use, we’ll have a better understanding of how this feedback may be impacting sentiment toward other areas of the business.
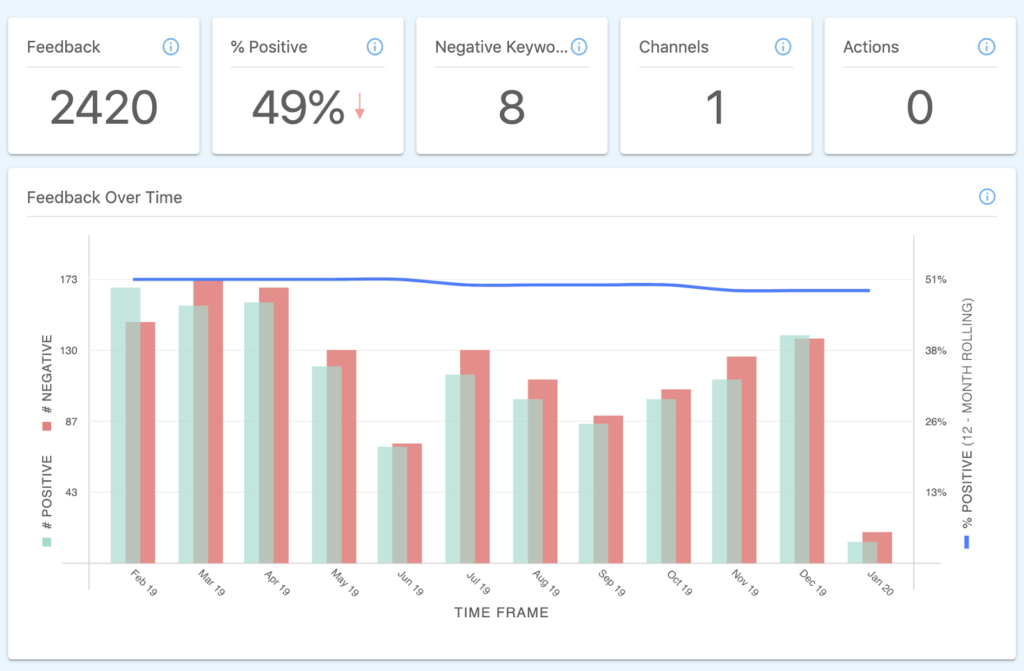
Step 2: Understand if the identified feedback trend is getting better or worse over time.
It’s clear from the 12-month rolling view that feedback related to Ease of Use has been trending negative over time, indicating that there are product issues that need to be addressed.
It could be that your product is too robust for a subset of your customers, or that users are having to work too hard to make the product work for them. We’ll dig into the common themes coming up in customer feedback next.
Step 3: Identify the problem
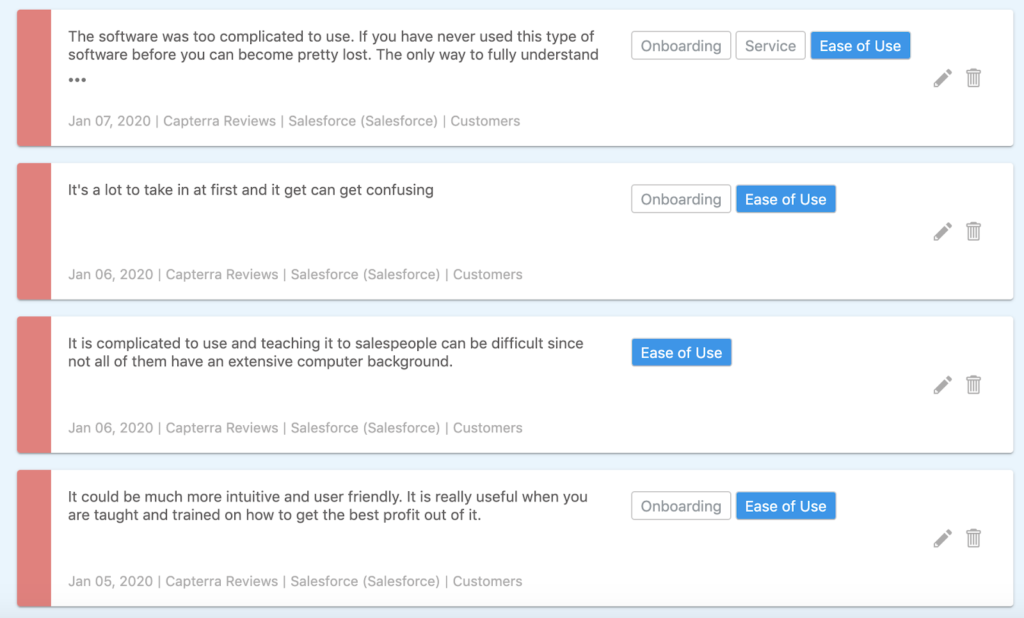
Now that we’ve identified an ongoing negative feedback trend, we will drill into the verbatim feedback related to this topic to understand the common issues coming up in customers’ feedback.
We recommend digging specifically into the following keyword mentions:
- UX
- UI
- Issues with new features
- Time to ramp
- Load time
- Performance
- User friendly
3. Benchmark feedback against competitors to put the issue in perspective
Rather than immediately dismissing the problem as a non-issue or jumping into action, we advise customers to do a bit more research to gather context and perspective.
Understanding how this customer feedback compares to competitor feedback will help you understand both the risk and opportunities this feedback represents to your business.
Step 1. Connect competitor feedback in Loop
Start by identifying comparable and aspirational companies in your industry, whether they are directly competing with you now or could be in the future. You can leverage online review sites like G2 Crowd and Capterra to see what companies the market is comparing you to today.
You can navigate to the Competitive Benchmarking dashboard from the Insights Overview sub navigation bar. Follow the link labeled, “Benchmark.”
Adding competitors to your dashboard will provide you with real-time updates on their customer feedback, giving you a more comprehensive view into what is and is not working for them.
Step 2. Compare negative feedback trends to competitors
Now that your competitor feedback has been added, you can benchmark your product feedback trends to competitors.
This will help you understand if competitors’ customers are expressing similar sentiment related to Ease of Use. You’ll then want to dig into your competitors’ UX and features offered to understand how the user experience and product offering differs.
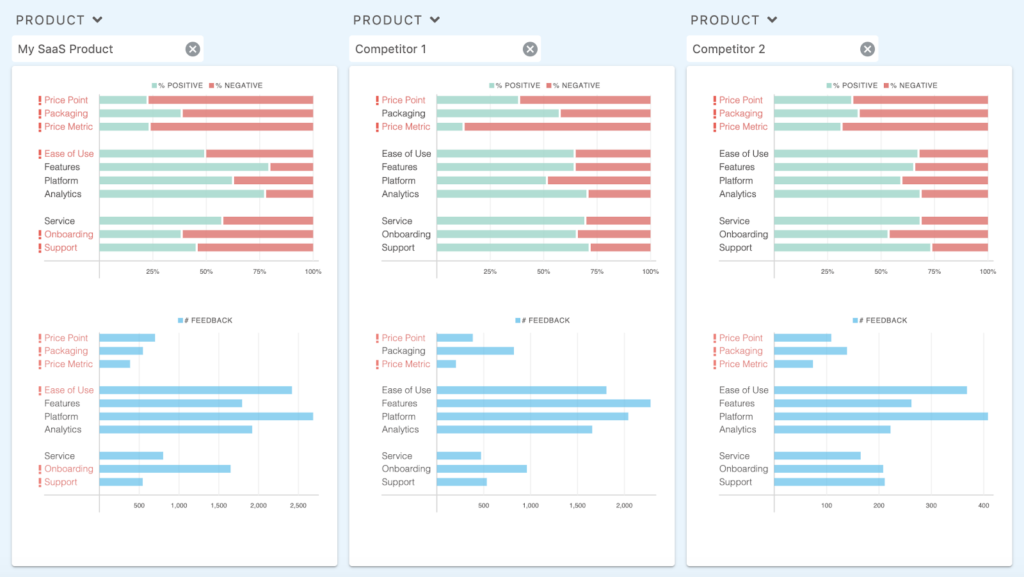
Comparing to Competitors:
First, we can see that feedback related to Pricing trends negative across the space, but that My SaaS Product is the only product trending negative in across topics such as Ease of Use, Onboarding, and Support.
This is an immediate flag that users are struggling to use the product as intended, and that this problem likely begins at onboarding.
Step 3. Make decision on taking action
From digging into the customer feedback data, we now know the following:
- Feedback related to Ease of Use has been trending negative over time
- Customer feedback related to Ease of Use is more negative than competitors
- Negative feedback about Onboarding, Support, and Pricing show that this issue is negatively impacting the customer experience.
Our next step is to decide whether or not the feedback trends warrant action. Do this by weighing the risks of inaction:
- Feedback about Ease of Use continues to trend negative, impacting sales as well as customer retention.
- Competitors continue to roll out new easy-to-use features that customers want.
The best step forward is to address concerns about Ease of Use by creating Actions.
4. Adapt Product Strategies to Address Issues
As you begin to put plans in place to address product issues, it will be important to understand the root cause of the feedback, internal or external factors, and any steps that have been taken previously to address customer feedback.
Taking action will require cross-team collaboration to ensure that there is alignment on the need and owners for each action.
Step 1: Identify root cause and past initiatives
Work with cross-functional partners to identify contributing factors and understand if past actions have had an impact on the feedback trends.
Things that could be driving negative feedback about your Ease of Use:
- Time to market – did you make promises that have yet to be delivered on?
- Competitor offerings – has a competitor recently released features that your customers want or need?
- Bugs or Product Stability – are features not working as expected?
- New Feature Release – were new features released that require more customer training in order to realize value
- Lack of product innovation – are market changes meaning that product features are being unused or antiquated?
- Complicated UX – are customers having to click too many times to get to critical information?
- Copy Inconsistency – is your product terminology clear and consistent?
Understanding the root cause of customers’ product concerns is critical to charting a path forward to address the issue. Conversely, perhaps the issue was known—sales, retention, or usage rates were declining—but the reason for these dips was not. In this case, customer feedback trends are the proof points needed to align teams on why and how to address the problem.
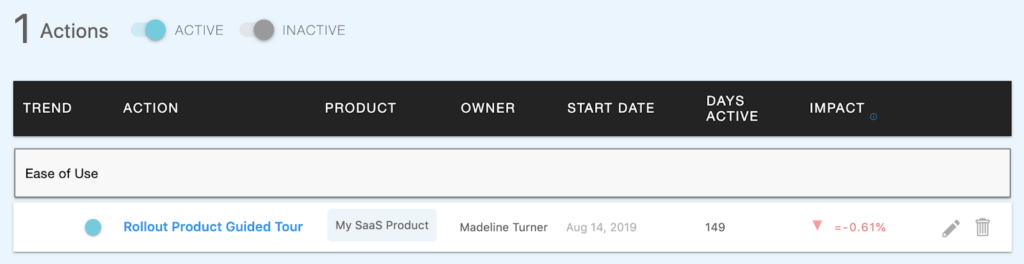
Once the root cause or past initiatives have been identified, create retroactive actions to mark the specific events contributing to the feedback trends.
Continuing our example, let’s assume the following:
- A product guided tour was rolled out in August
- Usage trends continue to show drop-off during primary product experiences, indicating confusion or too much work on users end to get to key features
We will want to create “past Actions” to chart the actions that have been previously taken to see their impact on sentiment over time. Then, we will create a new Action to track the impact of new initiatives.
Step 2: Create new initiatives to address the issue
Once you’ve identified the root cause of the issue and aligned stakeholders on the importance of addressing it, you’ll create specific action plans.
Here are example actions that may be taken to address negative feedback about your product’s ease of use:
- Ensure consistency of product and feature terminology
- Simplify UX by reducing UI clicks
- Model user roles based on value and features needed
- Update or remove features that are not being used
- Conduct user testing to understand roadblocks in product
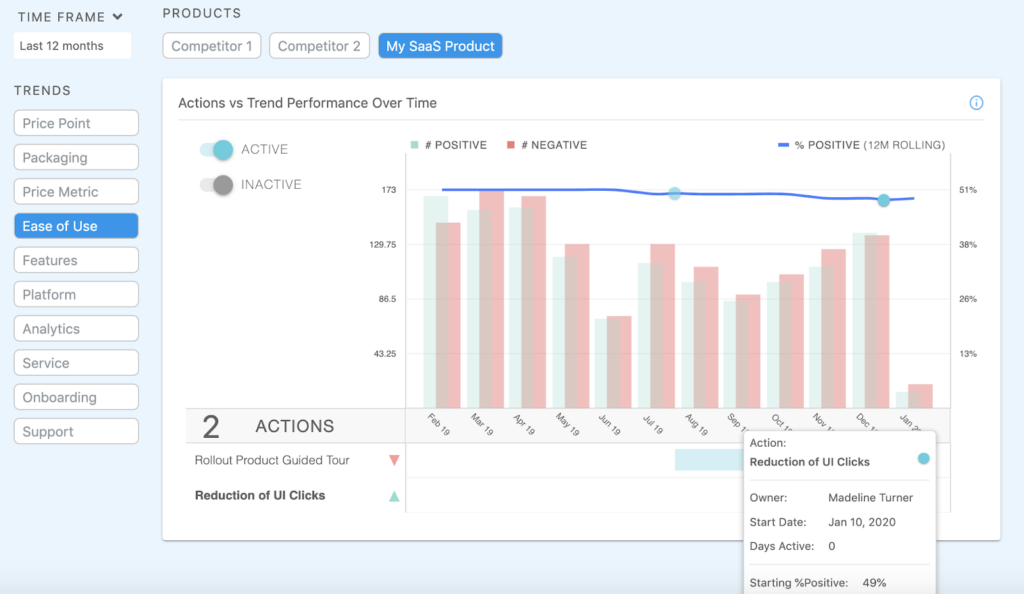
Continuing with our example, we know that the product tour hasn’t impacted customer feedback about the product’s ease of use, and based on usage trends, we can see that users are having to click too many times to get to the answer/key feature they need. We will address by updating the UI to limit the amount of user clicks.
Once you align on actions to be taken, create new Actions in Loop and assign owners for visibility. In this case, we’ve created an Action for “Reduction of UI Clicks.”
Step 3: Track the action to understand if it solves the issue over time
The final step is to measure the impact of your actions over time to ensure that you’re driving the intended outcome.
Set up regular cross-functional team meetings to review actions and progress to goals (ensure that there are area-specific metrics you’re measuring against like clicks or user behavior).
You should focus your meetings on answering whether existing actions are solving the problem or whether additional action needed.
Continuously monitor customer feedback to inform your Start/Stop/Continue plan:
- Start: What needs attention that doesn’t have an assigned action yet?
- Stop: Are actions you’ve taken having a negative impact on overall customer feedback?
- Continue: If actions you’ve taken are having a positive impact, continue investing in these initiatives and determining opportunities for expansion.
The key to using Loop to improve revenue and retention is following the four steps outlined above: listen for feedback, identify and understand trends, benchmark to understand risk and opportunities, and then adapt strategies to respond.